Converting ZIP codes to geographic coordinates is essential for applications like route planning, spatial analysis, and customer location mapping. ZIP codes are not precise geographic markers, but geocoding APIs like Zip2Geo can provide accurate latitude and longitude for better location-based decisions. Here's a quick guide:
- Why Do This? ZIP codes represent mail delivery areas, not exact locations. Geographic coordinates are more precise and reliable for tasks like distance calculations and navigation.
- How It Works: Use a geocoding API like Zip2Geo to convert postal codes into coordinates. This API supports over 100 countries, adheres to EU standards, and ensures GDPR compliance.
-
Key Steps:
- Understand ZIP codes and their limitations.
- Choose a geocoding service - hosted API (e.g., Zip2Geo) or local database.
- Set up and test the API, starting with a free plan for 200 requests/month.
- Integrate the API into your application for real-time or batch processing.
- Verify and use the results for tasks like delivery mapping or spatial analysis.
Pro Tip: For German and European users, ensure compliance with local formatting rules (e.g., decimal commas, metric units) and include ISO country codes like "DE" for Germany.
This method ensures accurate, up-to-date location data for your projects while meeting regional standards. The Zip2Geo API is easy to implement and scales for both small and large datasets.
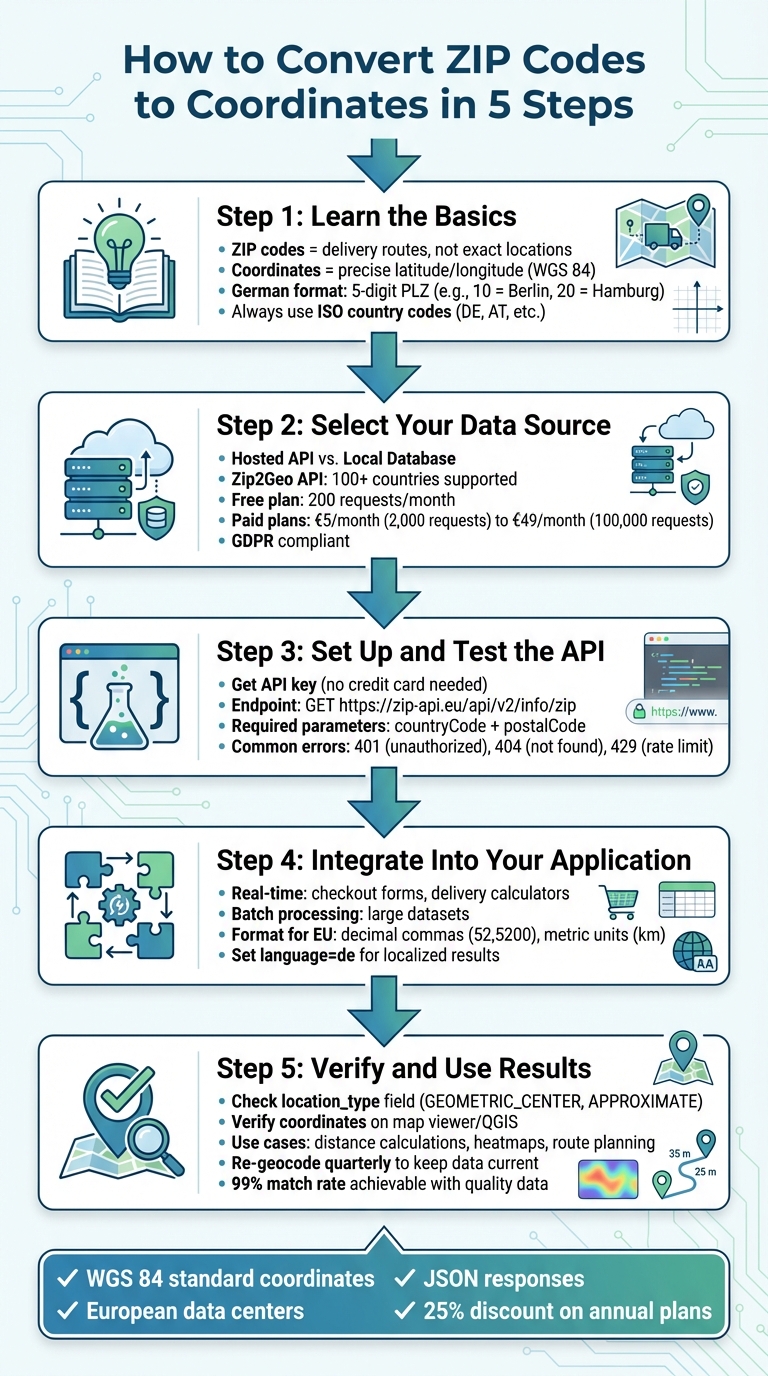
5 Steps to Convert ZIP Codes to Geographic Coordinates
Step 1: Learn the Basics of ZIP Codes and Coordinates
How ZIP Codes Work and Their Limits
In the U.S., ZIP codes follow a 5-digit hierarchical system. The first digit identifies a broad geographic region, the next two digits specify a processing hub, and the final two digits narrow it down to a local area. However, these codes are tied to delivery routes rather than fixed geographic boundaries. For example, two locations sharing the same 5-digit ZIP code might still be 10–20 kilometres apart in Germany. Understanding this framework is crucial when translating ZIP codes into precise coordinate data.
What Are Geographic Coordinates?
Since ZIP codes are not highly precise, geographic coordinates - latitude and longitude - become essential for pinpointing exact locations. These coordinates, based on the WGS 84 standard, are widely used by geocoding APIs like Zip2Geo. When a ZIP code is geocoded, the output is typically a pair of coordinates, such as 52.5200°N, 13.4050°E for Berlin's centre. Geocoding APIs often categorize results by accuracy: a "ROOFTOP" result indicates street-level precision, while "GEOMETRIC_CENTER" applies to broader areas like postal codes. Always check the location_type field in your API response to confirm if the result represents a specific point or the centroid of a larger area.
German and European Formatting Rules
When working with geocoded data in Germany or the EU, it's important to follow regional formatting standards. Germany uses 5-digit postal codes (PLZ, or Postleitzahlen), where the first two digits denote a general region - 10 for Berlin and 20 for Hamburg. Additionally, adhere to local conventions: use decimal commas, metric units, and the DD.MM.YYYY date format. To avoid confusion, always include the ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code (e.g., DE for Germany, AT for Austria) in your API requests. Without this, you might accidentally retrieve coordinates for Berlin, USA, instead of Berlin, Germany.
Step 2: Select Your Geocoding Data Source
Hosted API vs. Local Database
When converting ZIP codes into coordinates, you have two main options: a hosted API or a local database. Hosted APIs, such as Zip2Geo, are incredibly easy to integrate. They provide well-structured JSON endpoints, allowing you to send a request and receive coordinates without the hassle of setting up a server. On the other hand, local databases require more effort - they need manual setup, regular data synchronization, and dedicated hardware to run.
Hosted APIs offer the advantage of automated updates and effortless scalability, making them ideal for projects where speed and minimal maintenance are priorities. Whether you're working on mobile apps, websites, or backend systems, a hosted API can fit seamlessly into your tech stack. Local databases, however, are better suited for niche scenarios where having full control over your geographic data is a must.
What Zip2Geo Offers
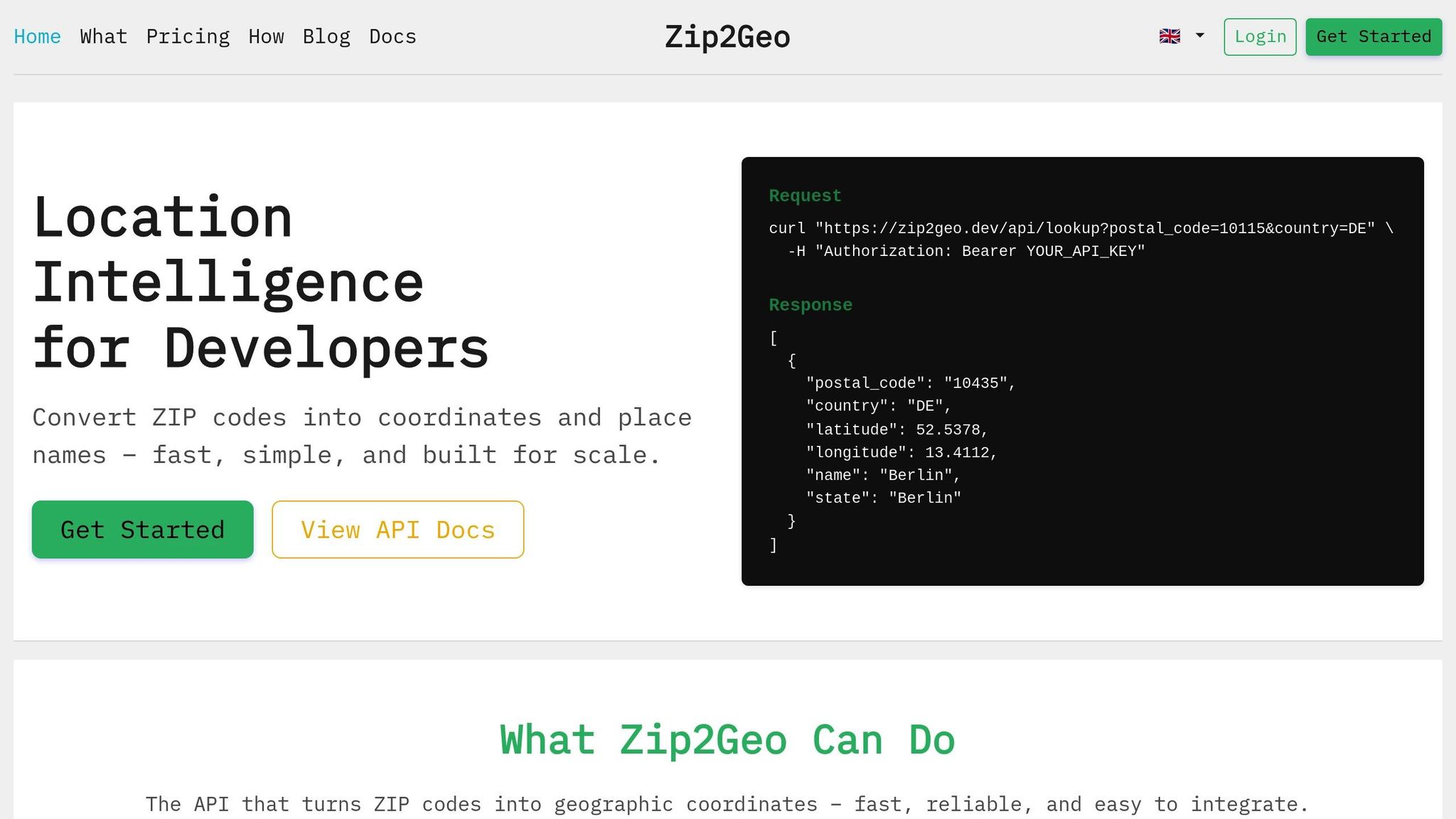
Zip2Geo takes these benefits a step further with its developer-friendly RESTful JSON API. It’s designed for those who need reliable geocoding without the burden of managing infrastructure. Supporting over 100 countries, including all of Europe, Zip2Geo delivers clean JSON responses packed with useful data - latitude, longitude, place names, regions, and country metadata. Plus, its response times are optimized for both live applications and batch processing.
For German and European users, pricing is structured in Euros. The Free plan includes 200 API requests per month, which is perfect for testing or small-scale projects. Paid plans start at just €5 per month for 2,000 requests, with options scaling up to €49 per month for 100,000 requests. Additionally, the platform is fully GDPR-compliant and relies on European data centers, making it a straightforward choice for EU-based projects.
Pick the Right Coordinate System
Once you've chosen your data source, ensure it uses a compatible coordinate system.
For the best compatibility with modern mapping tools, stick to the WGS 84 coordinate system. This global standard represents latitude and longitude in decimal degrees, and it’s the default format for Zip2Geo. WGS 84 integrates effortlessly with popular mapping platforms like Google Maps, OpenStreetMap, and Leaflet, ensuring your coordinate data works seamlessly across different tools and applications.
Geocoding for Beginners
Step 3: Set Up and Test the Zip2Geo API
Now that you’ve chosen your data source and understand the configuration, it’s time to integrate and test the API.
Get Your API Key
Start by creating an account on the Zip2Geo website to generate your personal API key. The platform’s Free plan allows up to 200 requests per month, making it perfect for testing or smaller projects. The best part? You don’t need a credit card to sign up. Once your account is set up, head to your dashboard to find your API key. This token is essential - it authenticates all your requests.
If you need more than 200 requests, you can explore higher-volume plans directly in your dashboard, which also provides detailed pricing and privacy information.
Run Your First API Request
Testing the API is simple. The main endpoint for transforming ZIP codes into coordinates is:
GET https://zip-api.eu/api/v2/info/zip
Make sure to include your API key in the request header as a Bearer token:
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY
The API requires two key parameters: countryCode (use "DE" for Germany) and postalCode. For instance, to test Berlin’s postal code (10115), send a GET request with countryCode=DE and postalCode=10115. The API will respond with neat JSON data, including fields like latitude, longitude, placeName, and state. For Berlin, you might see coordinates like 52.5200 for latitude and 13.4050 for longitude. If you’re not ready to dive into coding yet, try using the Demo tool on the Zip2Geo website, which lets you test endpoints without even needing an API key.
Handle Errors and Format Output
Understanding common API errors can save you a lot of time troubleshooting. Here’s what to watch for:
- 401 (Unauthorized): Your API key is missing or invalid. Double-check your token.
- 404 (Not Found): The postal code doesn’t exist in the database.
- 429 (Too Many Requests): You’ve exceeded your plan’s request limit, often due to overlapping parallel API calls.
The API returns coordinates as JSON floats with decimal points (e.g., 52.5200). For applications in Germany, you’ll want to convert these to decimal commas (e.g., 52,5200) for proper formatting. Additionally, always use the correct two-letter ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 country code (like "DE" for Germany or "AT" for Austria) to avoid invalid requests.
sbb-itb-823d7e3
Step 4: Add ZIP Code Conversion to Your Application
Build Your Processing Workflow
Start by collecting postal codes, ensuring they are free of extra spaces and include the correct country codes, such as "DE" for Germany or "AT" for Austria. Use the Zip2Geo API's info/zip endpoint, providing both the countryCode and postalCode parameters to retrieve latitude and longitude data. This API is designed to return well-structured JSON responses, making it compatible with various tech stacks and easy to integrate into your application workflow.
To optimize your API queries, use the fields parameter to request only the specific data you need. This approach keeps responses streamlined and efficient.
Real-Time vs. Batch Processing
After setting up your workflow, determine whether real-time or batch processing suits your application's needs. Real-time lookups are ideal for scenarios like checkout forms or delivery calculators, where users input postal codes on the spot. These requests are processed immediately, ensuring a smooth user experience.
For larger datasets, batch processing is the way to go. It allows you to handle multiple postal codes sequentially or in parallel, depending on your API plan's limitations. However, high-volume processing requires careful management of simultaneous requests. If too many parallel calls are made, you might encounter a 429 status code, indicating you've exceeded your plan's simultaneous request limit. To prevent this, implement a queue system to regulate the flow of requests or consider upgrading to a higher-tier plan with increased capacity.
Batch workflows also need robust error-handling mechanisms. Be prepared for 404 errors (postal code not found) and 429 errors (rate limit exceeded). For temporary issues, such as an UNKNOWN_ERROR status, use exponential backoff - retry the request after a brief delay to avoid overwhelming the server.
Format Output for European Users
When presenting results to European users, ensure the output aligns with local formatting standards. The API's default measurement unit is kilometres (km). For German users, format numbers using a comma as the decimal separator (e.g., 52,5200 instead of 52.5200) and a dot for thousand separators. To provide localized place names and addresses, set the language parameter to "de", which ensures results like "München" instead of "Munich." Additionally, apply region biasing by including region=de in your requests to prioritize German-specific results.
The Zip2Geo API complies with GDPR, as it processes only public postal code data and avoids handling personal information. This makes it a safe choice for European applications. To maintain accuracy, avoid long-term caching of coordinate data, as the database is regularly updated to reflect the latest information. This ensures your application remains reliable and up-to-date.
Step 5: Check and Apply Your Coordinate Data
Verify Your Geocoded Results
Once your API setup is complete, the next step is to ensure the coordinates retrieved align with the intended postal code areas. After obtaining coordinates from the Zip2Geo API, take time to verify their accuracy before using them in production. The API includes a location_type field that indicates the precision of the result. For postal code lookups, you’ll often encounter "GEOMETRIC_CENTER" or "APPROXIMATE", which represent the centroid of the postal code area, not a specific building. While "ROOFTOP" precision is ideal, it’s rarely available for postal code-level geocoding.
To confirm accuracy, use visual tools like a map viewer or GIS software such as QGIS. For example, if you’re checking coordinates for postal code 10115, you’d expect the marker to fall in central Berlin. If it doesn’t, further investigation is needed. Additionally, review the partial_match flag in the API response. If it returns true, consider validating the data further by cross-referencing with official Deutsche Post records or asking users to confirm the suggested location.
For programmatic checks, examine the address_components array to ensure the postal_code matches your input. Avoid relying on formatted_address, as its structure can vary. Given Germany’s extensive five-digit postal code system, cross-referencing against official records adds another layer of precision.
How to Use Geocoded Data
Once verified, geocoded coordinates open up a range of possibilities for location-based applications. Here are a few ways you can put them to work:
- Distance calculations: Use the coordinates to measure the distance between a customer’s postal code and your warehouse or to define delivery zones. Results are already in kilometres, making them compatible with European standards.
- Heatmaps and spatial analysis: Visualise customer density, sales territories, or service coverage across Germany. Aggregating postal code coordinates can highlight high-demand areas and help optimise resources.
- Route planning: Accurate centroids are invaluable for planning multi-stop delivery routes or scheduling field services. This is especially useful in logistics, e-commerce, and supply chain management.
While using geocoded data, ensure compliance with GDPR regulations. The Zip2Geo API processes only public postal code data without handling personal information, making it a suitable choice for European use. However, when creating customer-facing features, maintain transparency about how location data is used and stored. Even though postal codes aren’t considered personal data under GDPR, clear communication builds trust.
The usefulness of geocoded data depends on its accuracy and relevance, so keeping it up-to-date is essential.
Keep Your Data Current
After your initial setup and verification, it’s crucial to maintain the accuracy of your data. Postal systems are not static - new postal codes are introduced, boundaries shift, and administrative changes occur. Germany’s postal code system is updated periodically by Deutsche Post, meaning coordinates that were accurate a few months ago might no longer reflect the current layout. To stay ahead, re-geocode your postal codes every quarter or whenever inconsistencies arise.
Keep an eye on error trends in your geocoded data. A noticeable increase in ZERO_RESULTS responses for previously valid postal codes could indicate outdated input data or retired postal codes. Investigate these cases promptly. High-quality German datasets can achieve a 99% match rate for address validation, so maintaining clean and current data is key. Regularly query the API or refresh your local cache at set intervals to ensure your application remains reliable and accurate.
Conclusion
Converting ZIP codes to coordinates can be straightforward with these five steps: understand the fundamentals of ZIP codes and coordinates, choose a dependable geocoding data source, set up the Zip2Geo API, integrate it into your application, and confirm your results. This method enables you to implement functionalities like delivery mapping or spatial analysis while adhering to German and European standards. This streamlined process fits seamlessly into your workflows and delivers accurate geocoding tailored to European requirements.
The Zip2Geo API works effortlessly with any tech stack, offering clean JSON responses and full GDPR compliance. With coverage spanning over 100 countries and detailed support for German postal codes, you’ll have access to constantly updated data.
Take advantage of the free tier, which includes 7,000 API requests per month, and explore predictable pricing options. Annual subscriptions even include a 25% discount, making it a cost-effective solution. Whether you need to validate addresses in real time or handle large datasets through batch geocoding, Zip2Geo is built to handle both scenarios with ease.
Ensure accuracy by regularly verifying your data, managing errors, and staying up to date. Since German postal codes often represent zones rather than specific buildings, using an API that provides location types and confidence indicators is crucial for making well-informed decisions about data precision.
FAQs
Why is geocoding more accurate than relying on ZIP codes for location data?
Geocoding transforms a specific address into precise latitude and longitude coordinates, pinpointing exact geographic locations. On the other hand, ZIP codes cover broader postal regions, often encompassing multiple neighborhoods or areas. This distinction makes geocoding a much more accurate tool, especially when precision is key for working with detailed geospatial data or location-based applications.
With geocoding, tasks like mapping, routing, and analyzing location data become far more precise. It ensures results are tied to the exact address rather than a general postal area, delivering a higher level of accuracy for your projects.
What factors should I consider when choosing a geocoding API for my project?
When choosing a geocoding API, it's essential to match it with your technical needs and budget. Start by reviewing the pricing structure, usually displayed in euros (€), and any limits on requests. For instance, some APIs charge per 1,000 requests and might impose daily caps, which could be a concern for larger projects. Calculate your estimated usage - say, 10,000 requests monthly - and figure out the potential costs, which might range from €10,00 to €20,00 depending on the provider.
Next, assess the API's features to ensure they align with your needs. A good API should deliver precise latitude and longitude coordinates in decimal format, detailed address breakdowns, and localisation options. For example, it should allow biasing results for German postal codes or provide responses in German. If your project involves processing large datasets, look for batch processing capabilities to handle multiple ZIP codes or addresses efficiently.
Don't overlook security. Protect your API usage by implementing API keys with restrictions, such as limiting access to specific IP addresses, to guard against unauthorised access. Lastly, check if the API documentation is available in German and supports metric units like kilometres. This can make integration smoother and more user-friendly for your team.
How can I keep my geocoded data accurate and up to date?
To keep your geocoded data accurate and current, start by choosing a trustworthy geocoding service and making sure your input data is well-formatted. Clear and complete addresses reduce errors and improve the quality of your results. Set up a regular update schedule, such as quarterly or semi-annually, to refresh your data. This helps account for changes like updated postal codes or new addresses.
It's also helpful to store the date of each geocoding request (e.g., 15.03.2026). This allows you to track when updates are due. Keep an eye on API responses for any changes, such as error codes or updated information, so you can quickly address issues like new streets or altered postal codes.
To optimise performance, implement caching with a defined expiration period. This reduces unnecessary API calls while maintaining data accuracy. Additionally, stay up-to-date with your geocoding tool's documentation to be aware of any changes that might affect your results.