Understanding latitude and longitude is essential for building location-based applications. These coordinates power features like delivery tracking, route optimization, and address verification. Geocoding converts addresses into coordinates, while reverse geocoding transforms coordinates back into readable addresses. Tools like the Zip2Geo API simplify this process by offering fast, accurate data for over 100 countries.
Key Takeaways:
- Geocoding Basics: Latitude measures north-south positions, longitude measures east-west. Formats include Decimal Degrees (DD) and Degrees, Minutes, Seconds (DMS).
- Common Challenges: Handling partial matches, API errors, and inconsistent data formats.
- Optimization Tips: Use caching, region biasing (e.g., "de" for Germany), and exponential backoff for retries.
- Zip2Geo API: Offers forward/reverse geocoding, JSON responses, and plans starting at €5,00/month for 2,000 requests.
- German-Specific Considerations: Follow GDPR, use local address formats, and encode special characters like Umlauts.
By integrating reliable APIs and following best practices, you can ensure precise and efficient location data handling in your applications.
How to Use Google Maps API in Python | Geocoding, Reverse Geocoding, and Calculating Distance
Latitude and Longitude Basics
Latitude and Longitude Coordinate Systems Comparison: DMS vs DD Formats
What Are Latitude and Longitude?
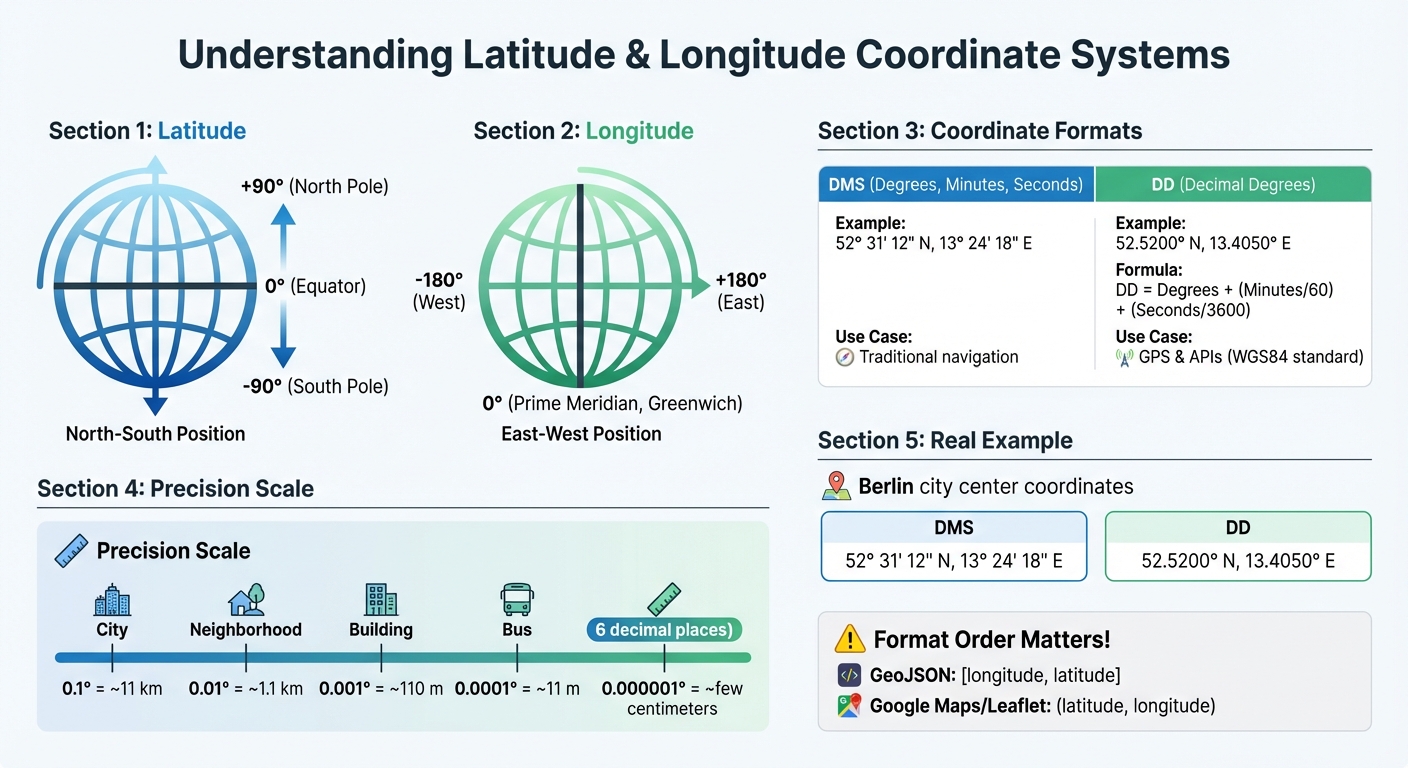
Latitude defines a location's position north or south of the Equator. The Equator itself is marked at 0°, with values increasing to +90° at the North Pole and decreasing to –90° at the South Pole. Longitude, on the other hand, measures how far east or west a point is from the Prime Meridian, which runs through Greenwich, London. Longitude ranges from 0° at the Prime Meridian to +180° eastward and –180° westward. Both latitude and longitude are angular measurements: latitude is the angle between a location and the equatorial plane, while longitude is measured in the equatorial plane relative to the Prime Meridian.
To make these measurements useful, they need to be tied to a model of Earth's shape. The most widely used model is WGS84, which is also the standard for GPS. Developers encounter two main formats for these coordinates: Degrees, Minutes, and Seconds (DMS) and Decimal Degrees (DD). To convert DMS to DD, use this formula:
DD = Degrees + (Minutes/60) + (Seconds/3600). For high precision, coordinates with six decimal places (0.000001 degrees) can pinpoint locations with accuracy down to a few centimetres.
How Geographic Coordinates Work
Geographic coordinates combine latitude and longitude to specify precise locations. For instance, Berlin's city centre is located at 52.5200° N, 13.4050° E. Germany's northernmost point, List on the island of Sylt, is at 55.050° N, 8.400° E, while the southernmost point, Haldenwanger Eck, sits at 47.270° N, 10.178° E. These coordinate pairs are universally recognized and machine-readable, making them crucial for global applications.
However, developers need to be mindful of formatting differences. GeoJSON uses the order [longitude, latitude], while platforms like Google Maps and Leaflet expect (latitude, longitude). Mixing these formats can cause integration errors. For distance calculations, the Haversine formula is useful for approximations on a spherical Earth, but Vincenty's formulae offer more precision by accounting for Earth's slightly flattened shape. For example, the distance from pole to pole is about 21 km shorter than the equatorial diameter. Understanding these nuances is essential when building applications that rely on geographic data.
Practical Applications for Developers
Latitude and longitude power a wide range of location-based applications. Mapping tools and visualizations use these coordinates to place markers, adjust viewports, and create custom store locators. In logistics and fleet management, coordinates help optimize delivery routes, calculate distances between drivers and customers, and provide accurate travel-time estimates.
Geocoding plays a vital role in address verification and fraud prevention. By converting coordinates into real-world addresses, businesses can validate shipping details or detect fraudulent transactions in real time. Similarly, reverse geocoding transforms raw GPS data into readable addresses, improving user experience in apps for delivery services or ride-sharing. Mastering these concepts is the first step to integrating API-driven solutions that expand your application's capabilities. Up next, we'll dive into how to implement these ideas with the Zip2Geo API.
Tools and APIs for Latitude/Longitude Lookups
Zip2Geo API Overview
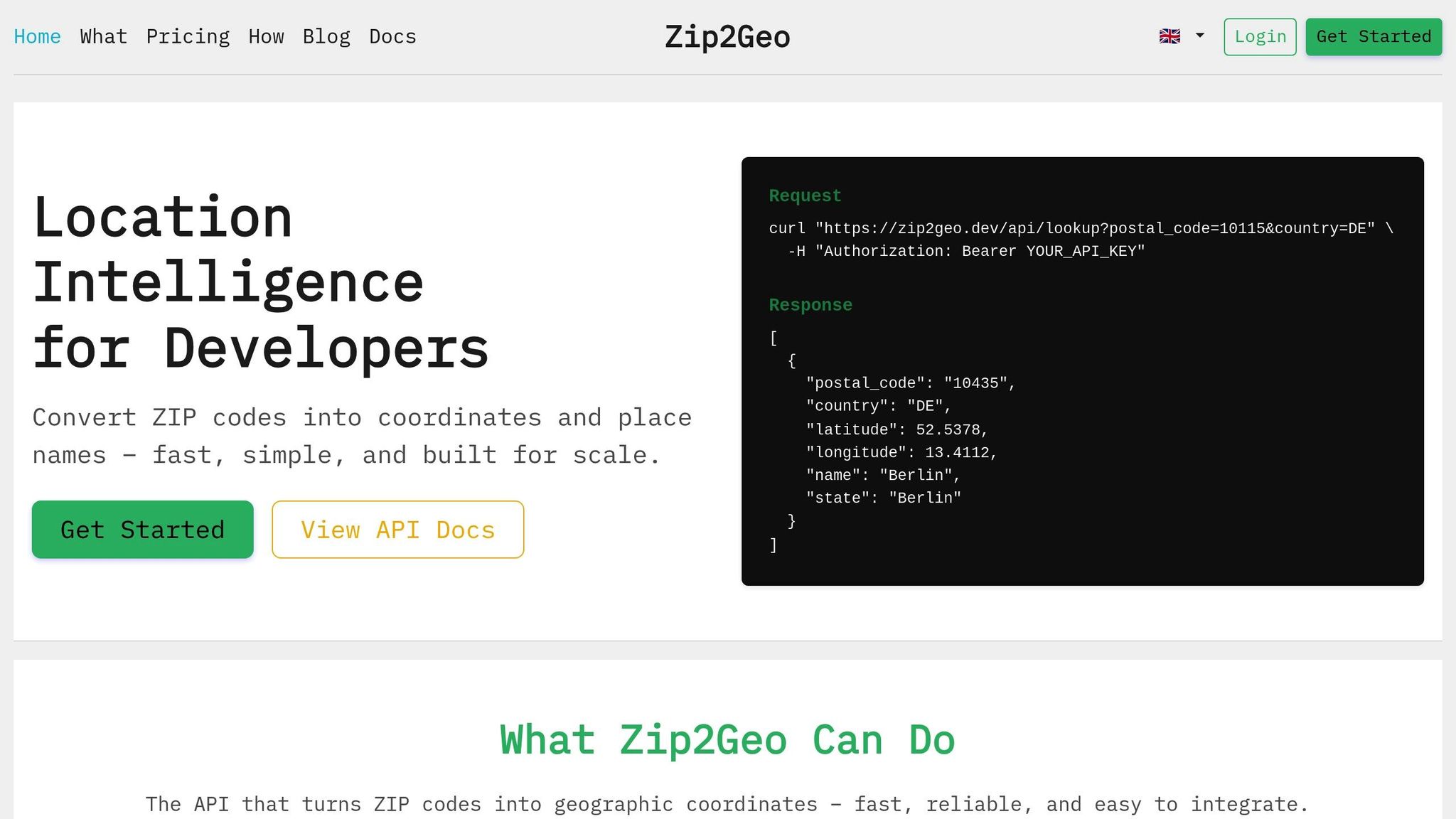
The Zip2Geo API is a powerful tool that transforms postal codes into accurate geographic coordinates, saving you the hassle of building a geocoding solution from scratch. Instead of spending months collecting datasets and creating a custom system, you can quickly integrate location intelligence using its RESTful HTTP interface, which delivers structured JSON responses. Plus, it takes care of data updates and maintenance automatically.
Covering postal codes from over 100 countries, Zip2Geo provides not only latitude and longitude but also additional details like city, state, and country. With response times measured in milliseconds, it’s ideal for both real-time applications and large-scale batch processes. By aggregating open data sources, the API ensures consistent performance across various regions worldwide.
Using the Zip2Geo API
To get started, you’ll need a 30-character alphanumeric API key. Once you have it, you can access versioned endpoints via HTTP GET, supplying parameters for authentication and location queries.
Zip2Geo supports two main functions: forward geocoding (turning postal codes or addresses into coordinates) and reverse geocoding (converting coordinates into readable addresses). To make integration even easier, the API provides SDKs for over 40 programming languages and frameworks. These SDKs handle tasks like URL encoding and authentication, significantly cutting down the time needed to integrate the API into your system.
For testing, Zip2Geo offers a free tier with 200 requests per month - no credit card required. Paid plans start at just €5,00 per month for 2,000 requests and go up to €49,00 per month for 100,000 requests. Higher-tier plans include SLA guarantees and access to dedicated support channels.
With these tools in hand, you’ll be well-prepared to optimize your geocoding workflows.
Zip2Geo API Features and Benefits
Zip2Geo goes beyond basic geocoding by offering rich metadata, such as time zones, currency information, road types, and speed limits - details that would take significant resources to maintain in-house. The API also provides data in multiple formats, including JSON, XML, and GeoJSON, ensuring compatibility with modern application architectures.
Building a custom geocoding solution can be a challenging and resource-intensive process. Zip2Geo eliminates that complexity by managing data updates and scaling for you. Unlike custom systems, it offers predictable pricing and enterprise-level scalability. For applications where precision is critical, Zip2Geo can even deliver "ROOFTOP" accuracy, pinpointing specific street addresses with remarkable detail.
sbb-itb-823d7e3
Best Practices for Latitude/Longitude Lookups
Optimizing API Requests
To make your latitude/longitude lookups efficient, consider caching frequently requested coordinates locally, but ensure this aligns with the API's caching policies. This reduces redundant requests and speeds up responses.
Avoid making synchronized requests in bulk. Instead, introduce a slight random delay (jitter) to spread out the calls evenly and prevent overwhelming the API. When errors occur, use an exponential backoff strategy: start with a short delay, like 100 milliseconds, and double it with each retry.
For faster results and reduced server load, handle geocoding requests directly in the browser. This also helps consider the user's regional context, which can improve the relevance of the results. Once you’ve optimized your requests, double-check that the returned coordinates meet the accuracy standards your application requires.
Validating Data Accuracy
Accuracy is key when dealing with location data. Pay close attention to the API's location_type field. A value like 'ROOFTOP' indicates pinpoint precision, while 'APPROXIMATE' or 'GEOMETRIC_CENTER' suggest less reliable results. Additionally, check the partial_match flag to identify whether the results are approximations. For critical use cases - like delivery logistics or emergency services - it’s wise to reject partial matches and prompt users to verify their input.
To improve accuracy further, use component filtering. For example, restricting searches with ISO 3166-2 country codes can help avoid confusion with places that share the same name. If you're searching for "Frankfurt", this method ensures you get Frankfurt am Main rather than a similarly named location elsewhere.
These validation steps not only improve the reliability of your data but also help you stay compliant with regional rules and expectations.
Complying with Local Regulations
When working with users in Germany, be mindful of their strong focus on privacy. Share only the minimum amount of location data necessary. To comply with GDPR, always use HTTPS, limit data storage to essentials, obtain explicit opt-in consent, and respond promptly to deletion requests.
Additionally, ensure that German-specific details are handled correctly. Encode Umlauts (ä, ö, ü) properly and follow the local address format: street name, house number, five-digit postal code, and city (e.g., "Hauptstrasse 10, 10115 Berlin"). If you’re aggregating geocoded data for analysis, consider grouping it by NUTS-3 level regions (counties and districts). This aligns your data with official German government standards, ensuring consistency and compliance.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Dealing with Missing or Incorrect Data
Inaccurate geolocation data can seriously affect the reliability of applications. Common problems include high error rates from IP-based coordinate conversions, multipath errors caused by physical obstructions, and inconsistencies in address formats - like missing directional prefixes, reversed street numbers, or unusual layouts - that lead to geocoding failures.
To tackle these issues, prioritize GPS data collected via SDKs over less reliable methods. Use smart filters to identify and disregard sudden, unrealistic location shifts. Standardize address data with natural language processing (NLP) before sending it to a geocoding API. GPS-enabled smartphones generally provide accurate location data within a 4.9-metre radius when used under an open sky. If GPS data isn’t available, rely on network-based positioning using Wi-Fi or cell towers, or give users the option to manually correct their location.
"The quality of address points is as important as the data itself. Low-quality points can lead to inaccurate geocodes, placing addresses in the wrong locations, like dropping you off in the middle of a street instead of at the doorstep." - Skip Cody, Product Manager, LightBox
After addressing data accuracy, let’s look at performance issues that can also impact geocoding results.
Fixing Performance Issues
Performance bottlenecks often arise when the wrong tools are used for specific tasks. For real-time user input, leverage the Places API Place Autocomplete service. It’s designed for minimal latency and effectively handles typos. When working with the Directions or Distance Matrix APIs, use Place IDs instead of full address strings. This eliminates an extra internal geocoding step, speeding up response times. These strategies align with earlier optimization techniques to ensure your application processes location data efficiently.
To manage API quotas and prevent overloading, introduce random delay intervals to distribute requests evenly. For batch processing static datasets, server-side geocoding is often more suitable. On the other hand, client-side geocoding tends to perform better for interactive user tasks.
While performance is key, tailoring results to local formats is just as important.
Adapting to Local Formats
For applications in Germany, ensure all data adheres to local conventions. Use commas as decimal markers (e.g., 52,520°) and dots for thousand separators (e.g., 1.000 requests). Display dates in the DD.MM.YYYY format (e.g., 13.01.2026) and times using the 24-hour clock. When showing distances, stick to metric units like kilometres and metres, and display temperatures in Celsius.
Address formatting should follow the Deutsche Post standard: street name, house number, five-digit postal code, and city. By aligning your application with these conventions, you enhance user experience and ensure the data feels natural and relevant to local users. This builds on the core principles discussed earlier, helping your application deliver precise and reliable location data.
Conclusion
Main Takeaways
Accurate geocoding plays a crucial role in developing dependable location-based applications. By understanding how latitude and longitude coordinates function - and knowing when to apply forward or reverse geocoding - you’ll be well-equipped to manage location data with confidence. The Zip2Geo API offers a simple yet powerful solution, covering over 100 countries worldwide. It provides geographic coordinates and place names via a RESTful interface with response times measured in milliseconds. Starting at just €5,00 per month for 2,000 requests, it caters to everything from small projects to enterprise needs with plans supporting up to 100,000 requests monthly.
To get the most out of geocoding, consider using Place IDs, validate precision with location_type metadata, and apply region biasing for contextually relevant results. Address potential pitfalls early: prioritize GPS data over IP-based methods, normalize address formats with NLP before geocoding, and use exponential backoff strategies for handling temporary errors. For users in Germany, ensure compliance with local address formatting standards. By following these proven approaches, your application can consistently provide accurate and reliable location data.
Next Steps
Start by signing up for a Zip2Geo account to get your API key. The free tier, offering 200 requests per month, is a great way to begin testing. Opt for JSON responses to minimize payload size and simplify data parsing. If your app processes real-time user input, consider combining Place Autocomplete services with standard geocoding to strike the right balance between speed and accuracy.
Put the optimization tips into action: use client libraries for authentication and retry logic, secure your requests with HTTPS, and percent-encode special characters when needed. Keep an eye on your API usage and upgrade your plan as your application grows. With these strategies and tools at your disposal, you’re ready to build location-based features that deliver reliable and precise results to your users.
FAQs
What measures does the Zip2Geo API take to handle geocoding errors and ensure accurate data?
The Zip2Geo API is built to handle geocoding challenges effectively while maintaining precise data output. It incorporates sophisticated validation techniques to identify and fix issues like misspelled addresses or incomplete data entries.
To achieve reliable results, the API cross-checks information across various databases and integrates error-handling protocols. These protocols include fallback methods to manage cases where the results might be unclear. On top of that, the API provides detailed error codes and messages, making it easier for developers to identify and resolve issues. This streamlined approach helps enhance the overall user experience in applications that rely on geocoding.
What makes the Zip2Geo API a better choice than building your own geocoding solution?
Using the Zip2Geo API takes the hassle out of building and maintaining your own geocoding system, saving you both time and resources. With its simple REST endpoint, the API lets you perform accurate latitude and longitude lookups using just an API key and a URL request. That means no more worrying about sourcing, cleaning, or updating geocoding data - it’s all handled for you.
This service is built to scale and is highly reliable, capable of managing traffic surges without requiring you to deal with server management, load balancing, or caching. Plus, Zip2Geo provides SDKs for more than 40 programming languages, making integration smoother and reducing the chances of errors. With its clear documentation, practical guides, and example queries, you can implement geocoding efficiently and focus on improving your app’s core features instead of wrestling with infrastructure headaches.
What are the best ways for developers to optimise API requests for better performance and efficiency?
To make latitude and longitude lookups more efficient, treat every API request as a resource to be used wisely. Start by using batching to combine multiple address queries into a single request. Pair this with caching - store frequently used results locally, whether in Redis or a simple file. This reduces redundant lookups, keeps your API calls to a minimum, and helps you stay within usage limits.
When sending requests, prioritize efficiency by limiting responses to only the fields you need, like lat,lng. You can also use geographic filters such as bounds or region to focus the search area. These steps not only speed up the process but also help conserve your API quota. Don't forget to follow best practices for web services: always use HTTPS, handle errors properly (e.g., implement exponential back-off for retries), and respect rate limits to avoid disruptions.
Keep an eye on your API usage, monitoring it regularly - daily checks work well, such as at 12.01.2026. Set up alerts for cost thresholds, like €0.50 per 1,000 requests, to avoid unexpected expenses. By combining caching, filtering, and smart scheduling, you can offer fast, cost-conscious location-based services tailored to the needs of users in Germany.